We all know that a control system manages or directs the operation of a system in order to provide a specific output. In a closed-loop system, the desired output is achieved by making a comparison between achieved output and provided input.
And for this purpose, a part of the output is fed back to the input in order to have the difference in the input and output value. This is known as a feedback signal.
Thus we can say the system whose operation is controlled by its output is known as a closed-loop control system.
We have already discussed a closed-loop control system in our previous article so to have a detailed idea of operation you can refer the same. Here we will discuss the examples along with the advantages and disadvantages of closed-loop systems.
Here we will discuss the detailed operation of an automatic electric iron and a temperature control system.
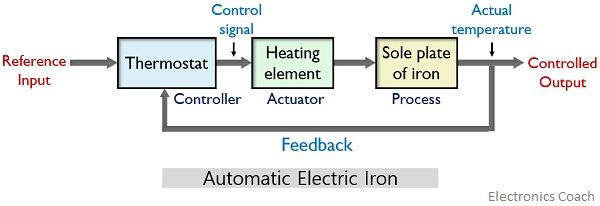
Consider an example of automatic electric iron which acts as a closed-loop system. The figure below represents the block diagram with major components:

An automatic electric iron consists of a thermostat that acts as a controller of the system, a resistive heating element is present that generates heat.
The sole-plate of the iron instrument acts as a process of the overall system.
The basic working performed by an automatic electric iron is such that when the temperature of the sole-plate attains a predefined value then the heating action gets stopped automatically. And when the temperature falls below a certain specified value then again heating starts inside it.
So, it is clear that in this type of system the controlling depends on the output of the system.
Initially, in electric iron, the thermostat is provided with a certain specific value which acts as a reference input for the system.
When the input is provided to the system, then the resistive heating element generates heat inside the system. This leads to rising up the temperature of the iron sole. Through a feedback element, this output temperature is compared with the reference input of the thermostat.
If the achieved output shows lesser value than the reference input, then the difference temperature actuates the thermostat and this switches on the heating element.
This resultantly causes an increase in the temperature of the iron sole.
Once the temperature exceeds the reference value then the heating element automatically turns off. And after a certain point of time, the temperature starts to decrease.
However, the comparison still goes on and as the temperature falls below the specific value, the heating element again begins to raise the temperature of the sole.
In this way the continuous process inside an electric iron takes place.
Let us now take another example of a temperature control system that functions as a closed-loop system.
The main purpose possessed by a temperature control system is to maintain a constant temperature of water. Generally, these systems are used to provide an invariable temperature (hot) at the output.
The figure below represents the block diagram representation of a closed-loop system:
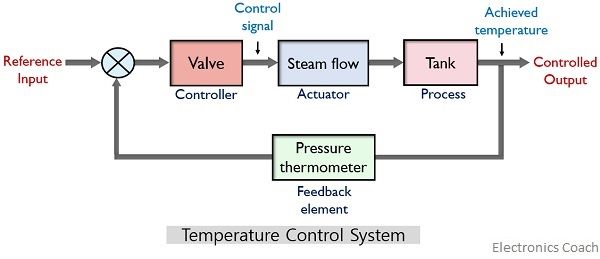
Basically in such type of systems water from an outlet come with a constant flow rate. Also, internally generated steam from a valve is mixed with the water to have a predetermined temperature of water.
A pressure thermometer is used inside the system that acts as feedback. So, when a reference input is provided to the system then the valve present generates a control signal that indicates the system to provide the required amount of steam.
When the steam mixes with the water coming from the outlet then the temperature of the water is measured by the pressure thermometer and is compared with the reference input given to the system.
If the desired temperature (reference input) shows equivalency with the generated temperature, then the control signal is generated and the flow of steam is stopped.
But if some amount of variation exists between the two temperature values then the controller generates the control signal regarding the level of temperature difference which is further compensated during the process.
In this way, the continuous process inside the system takes place and a controlled level of temperature is maintained.
In our day to day life, we come across various uses of closed-loop systems. From an air conditioner that manages to provide the desired value of room temperature by making required adjustments to automatic washing machines that provide the required level of dryness to the cloth after washing.
In a similar way from an automatic toaster, water level controller, home heating system to dc motor speed control and missile launching system, etc. everything that is designed to generate the required output with accuracy is the closed-loop system.